Enhancing Patient Experience
Enhancing patient experience in healthcare is crucial for both patients and medical practices. When patients feel valued and cared for, they are more likely to return for future visits and recommend the practice to others. This positive feedback loop not only helps patients receive better care but also supports the growth and sustainability of small to mid-size private practices. However, these practices face significant challenges in today’s healthcare landscape, especially when it comes to attracting new patients.
In recent years, many small medical practices have struggled to keep up with changes in marketing and patient engagement. As larger healthcare systems consolidate and dominate the market, independent practices often lack the resources to compete effectively. They may have limited budgets for marketing, making it hard to reach potential patients who are looking for quality care. Additionally, the increasing complexity of healthcare regulations and administrative tasks can take time away from patient interactions, further complicating efforts to improve patient experience.
Understanding the history of practice development is essential in recognizing these challenges. Over the past few decades, the healthcare industry has shifted dramatically, with more emphasis on patient-centered care and value-based payment models. This evolution has created opportunities for small practices to thrive by focusing on building strong relationships with their patients. However, it has also introduced new pressures that require innovative solutions.
In this case study, we will explore how enhancing patient experience can be a game-changer for private practices. We will identify the key challenges they face and present effective strategies that can help them connect with patients suffering from undiagnosed or latent diseases. By addressing these issues head-on, we aim to provide a roadmap for practices looking to improve their patient experience and ultimately grow their business.
Understanding Patient Experience
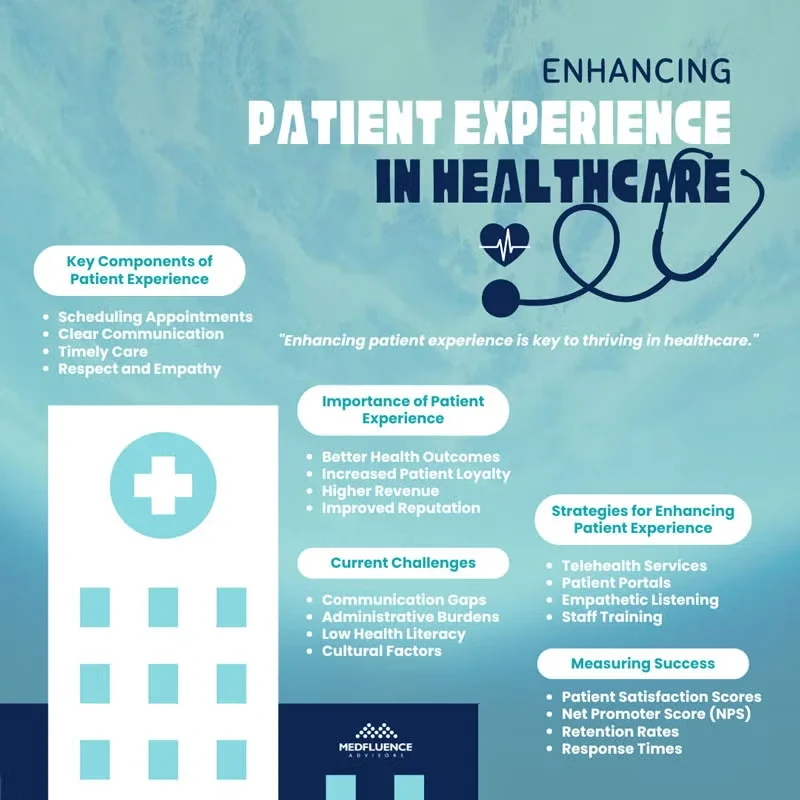
Patient experience refers to all the interactions that patients have with the healthcare system. This includes everything from scheduling appointments and talking to doctors to receiving treatment and following up afterward. It’s not just about how well a patient is treated during their visit; it also encompasses how they feel about their entire healthcare journey.
For example, did they receive clear communication from their healthcare providers? Were they treated with respect and empathy? These factors can greatly influence a patient’s overall impression of their care.
In essence, patient experience is about putting the patient’s needs, preferences, and values at the center of care. It involves every touchpoint in a patient’s healthcare journey, ensuring that they feel supported and cared for throughout their experience. This focus on patient experience is becoming increasingly important as more people take an active role in their healthcare decisions.
Importance of Patient Experience
The importance of patient experience cannot be overstated. Research shows that there is a strong connection between how patients perceive their care and the outcomes they experience. When patients have positive experiences—such as feeling listened to and receiving timely care—they are more likely to follow medical advice, which can lead to better health results. For instance, patients who trust their doctors are more likely to stick to treatment plans and attend follow-up appointments.
From a business perspective, improving patient experience is also crucial for healthcare practices. Happy patients are more likely to return for future visits and recommend the practice to others, which can help attract new patients. This loyalty can significantly impact a practice’s financial success. In fact, studies have shown that practices that prioritize patient experience often see increased revenue, improved reputation, and higher patient retention rates.
Enhancing patient experience is not only beneficial for patients but also essential for the growth and sustainability of healthcare practices. By focusing on creating positive interactions at every stage of care, healthcare providers can improve both clinical outcomes and their bottom line.
Current Challenges in Patient Experience
Patient engagement is essential for effective healthcare, but several barriers can hinder this process. One of the most significant challenges is communication gaps between patients and healthcare providers. When doctors and nurses do not communicate clearly or listen to patients’ concerns, misunderstandings can arise.
This lack of effective communication can lead to confusion about treatment plans and a feeling of disconnection from the care process. Moreover, administrative burdens—such as long wait times, complicated paperwork, and scheduling issues—can frustrate patients and discourage them from actively participating in their healthcare.
Other barriers include low health literacy, where patients may not fully understand their medical conditions or treatment options, making them less likely to engage in their care. Additionally, cultural factors can play a role; some patients may feel uncomfortable discussing their health due to cultural norms or past negative experiences with the healthcare system.
These barriers can significantly impact patient satisfaction and hinder the growth of healthcare practices. When patients are disengaged, they are less likely to follow treatment plans or return for follow-up visits, which can ultimately affect their health outcomes.
Case Examples
For instance, a small family practice reported low compliance rates among patients with chronic illnesses. After conducting surveys, they discovered that many patients felt overwhelmed by the amount of information provided during consultations. This led to confusion about medication regimens and follow-up appointments. By addressing the communication gap—simplifying explanations and providing written instructions—the practice saw an increase in patient adherence to treatment plans.
Another example involves a mental health clinic that received negative feedback regarding its intake process. Patients expressed frustration with long wait times and complicated forms that seemed unnecessary. As a result, many potential clients chose not to seek care at all. The clinic decided to streamline its administrative processes by implementing an online intake form that could be filled out before the appointment. This change not only improved patient satisfaction but also increased the number of new patients who sought services.
These examples highlight how addressing key barriers to patient engagement can lead to improved satisfaction and practice growth. By understanding and overcoming these challenges, healthcare providers can create a more supportive environment that encourages patients to take an active role in their health care journey.
Strategies for Enhancing Patient Experience
To enhance patient interactions, healthcare practices are increasingly adopting innovative technologies and practices.
Telehealth
One significant advancement is telehealth, which allows patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely. This convenience not only reduces travel time but also makes it easier for patients to access care, especially those with mobility issues or those living in remote areas. Telehealth has become particularly important in recent years, as it offers a safe way to receive medical advice and follow-ups without the need for in-person visits.
Patient Portals
Another valuable tool is patient portals, which are secure online platforms where patients can access their medical records, schedule appointments, and communicate with their healthcare providers. These portals empower patients by giving them control over their healthcare information and making it easier to manage their health. By providing clear and easy access to information, patient portals enhance engagement and satisfaction.
Empathetic Listening Techniques And Shared Decision-Making Models
Additionally, practices are implementing empathetic listening techniques and shared decision-making models to improve communication. By actively listening to patients and involving them in their care decisions, providers can foster a more collaborative relationship that enhances the overall patient experience. Research has shown that when patients feel heard and valued, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and recommend the practice to others.
Training and Development
Staff training plays a crucial role in improving patient-provider interactions. Training programs focused on communication skills, empathy, and cultural competence can significantly enhance how staff members engage with patients. For example, training that emphasizes active listening and understanding emotional cues can help staff connect with patients on a deeper level.
One successful training program involved a family practice that implemented workshops on empathetic communication. Staff learned techniques such as using open-ended questions and reflective statements to encourage patients to share their concerns more freely. After the training, the practice reported improved patient satisfaction scores and received positive feedback about the quality of interactions between staff and patients.
Implementing Change: A Step-by-Step Approach
Implementing change in a healthcare practice is essential for enhancing patient experience and ensuring long-term success. However, navigating this process can be challenging without a clear plan. A structured, step-by-step approach allows practices to effectively identify areas for improvement, develop targeted strategies, and monitor progress over time.
Assessment Phase
To effectively enhance patient experience, practices must first evaluate their current performance through patient experience metrics. This evaluation can involve collecting data from surveys, feedback forms, or focus groups that provide insights into patient satisfaction levels. Tools like the Patient Activation Measure (PAM) can help assess how engaged patients feel in their own care.
Gathering feedback is essential; practices can use various methodologies such as patient surveys, interviews, or observation of patient interactions. These tools allow healthcare providers to identify specific areas needing improvement and understand the factors contributing to patient dissatisfaction.
Action Plan Development
Once assessment findings are collected, the next step is creating a tailored action plan based on this data. This plan should outline specific strategies for improvement while setting measurable goals. For instance, if survey results indicate long wait times as a major concern, the action plan could include steps to streamline scheduling processes or improve staff efficiency.
Setting measurable goals is critical for tracking progress over time. Goals could include increasing patient satisfaction scores by a certain percentage or reducing wait times by a specific number of minutes within a defined timeframe.
Execution and Monitoring
Implementing changes requires careful execution within the practice. This might involve updating protocols, enhancing staff training programs, or integrating new technologies like telehealth services or patient portals.
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure that changes are effective. Practices should regularly review patient feedback and performance metrics to adapt strategies as needed. For example, if new communication techniques are introduced but do not lead to improved satisfaction scores, further adjustments may be necessary.
Measuring Success
Measuring success in healthcare is essential for understanding how well a practice meets the needs of its patients and achieves its goals. By evaluating patient experience and clinical outcomes, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement, demonstrate their value to stakeholders, and enhance overall care quality. A structured approach to measurement not only helps in tracking progress but also informs strategic decisions that can lead to better patient engagement and satisfaction.
In this section, we will delve into the concept of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which are critical metrics used to assess the effectiveness of patient experience initiatives and overall practice performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that help healthcare organizations evaluate their success in achieving specific objectives. In the context of patient experience, KPIs provide insights into how well a practice is performing in terms of patient satisfaction, engagement, and overall care quality. Here are some essential KPIs relevant to measuring patient experience:
- Patient Satisfaction Scores: These scores are typically gathered through surveys that ask patients about their experiences during visits. Common tools include the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey, which evaluates various aspects of care, including communication with doctors and nurses, responsiveness of hospital staff, and overall satisfaction.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): This metric measures the likelihood of patients recommending the practice to others. A high NPS indicates strong patient loyalty and satisfaction, while a low score may suggest areas needing improvement.
- Patient Retention Rates: This KPI tracks the percentage of patients who return for follow-up visits or ongoing care. High retention rates often reflect positive patient experiences and satisfaction with the care received.
- Referral Rates: The number of new patients referred by existing patients can serve as an indicator of patient trust and satisfaction. A higher referral rate typically suggests that patients are pleased with their care and willing to recommend it to friends and family.
- Patient Compliance Rates: This metric measures how well patients adhere to prescribed treatment plans or follow-up appointments. Improved compliance often correlates with better communication and engagement between healthcare providers and patients.
- Response Times: Tracking how quickly staff respond to patient inquiries or concerns can provide valuable insights into operational efficiency and patient satisfaction. Shorter response times generally lead to higher levels of patient trust and satisfaction.
By regularly monitoring these KPIs, healthcare practices can gain a clearer understanding of their performance in enhancing patient experience. This data-driven approach allows practices to identify strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to make informed decisions about where to focus their improvement efforts.
A Path Forward for Enhancing Patient Experience

Enhancing patient experience is not just a trend; it is a fundamental aspect of providing quality healthcare that benefits both patients and practices. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, small to mid-size private practices must prioritize patient engagement and satisfaction to thrive in a competitive environment. By understanding the key challenges—such as communication gaps and administrative burdens—healthcare providers can implement innovative strategies like telehealth and patient portals that foster better interactions.
Training staff to improve patient-provider communication and actively seeking feedback through structured assessments are essential steps in this journey. By establishing clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), practices can measure their success and make data-driven decisions that lead to continuous improvement.
Ultimately, creating a positive patient experience not only enhances clinical outcomes but also drives practice growth and sustainability. As healthcare providers embrace these strategies, they will be better equipped to meet the needs of their patients, build lasting relationships, and ensure a healthier future for all. The commitment to enhancing patient experience will pave the way for a more compassionate, effective, and successful healthcare system.


